Value-Added Tax (VAT) in Vietnam is an indirect consumption tax levied at each stage of the supply chain—from manufacturing, distribution, to final sale. It is designed to tax the “value added” at each point of the production and distribution process. VAT applies to most goods and services used for production, business, and consumption in Vietnam.
VAT Applies to the Following Activities in Vietnam:
-
Domestic supply of goods and services: Sales within Vietnam by local businesses.
-
Importation of goods: All goods imported into Vietnam are subject to VAT at the point of customs clearance.
-
Export-related services and activities: Some export services may be zero-rated or taxed depending on conditions.
-
Construction, leasing, and logistics: Including services provided by foreign contractors or cross-border entities.
Who Is Required to Register for Value-Added Tax in Vietnam?
Under Vietnamese tax law, the following entities are obligated to register for VAT:
-
Domestic enterprises: All businesses operating within Vietnam that manufacture, trade, or provide services.
-
Importers: Individuals or organizations importing goods into Vietnam must register and pay VAT at customs.
-
Foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs): Companies with foreign ownership conducting business in Vietnam, including representative offices if they engage in taxable transactions.
-
Foreign contractors: Overseas companies that provide goods or services to Vietnamese entities under contracts may need to register for VAT or pay through the Foreign Contractor Tax (FCT) regime.
-
E-commerce and digital service providers: Foreign entities without a permanent establishment in Vietnam that supply digital products or services directly to Vietnamese consumers are also required to register for VAT under recent regulations (Decree No. 132/2020/ND-CP and Circular 80/2021/TT-BTC).
VAT Rates in Vietnam (2025)
As of 2025, Vietnam’s Value-Added Tax (VAT) system includes three main VAT rates: 10%, 5%, and 0%, depending on the nature of the goods or services. Understanding these rates is essential for businesses to comply with Vietnamese tax regulations and apply the correct rate in invoices and VAT declarations.
| VAT Type | Rate (%) | Applicable Goods and Services | Purpose / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard VAT | 10% | Majority of goods and services: consumer goods (electronics, clothing, furniture), commercial services (consulting, advertising, legal), industrial products, processed food and beverages (excluding essentials) | Most commonly applied VAT rate for general goods/services |
| Reduced VAT | 5% | Essential goods and services: clean water for household use, unprocessed agricultural products, medical equipment and healthcare services, educational books and materials, scientific and technological services, social housing services | To reduce tax burden on essential sectors and vulnerable groups |
| Zero VAT | 0% | Exported goods and services, international transportation (air and sea freight), offshore outsourcing services, services provided to foreign entities (subject to conditions) | Encourages exports and international transactions, requires proper documentation |
VAT-Exempt Goods and Services in Vietnam (2025)
In addition to the three VAT rates, some goods and services are exempt from VAT entirely. This means they are not subject to VAT, and businesses cannot claim input VAT credits related to these transactions. Common VAT-exempt sectors include:
-
Financial and banking services (e.g., loans, interest income)
-
Public postal and telecommunications services
-
Education and vocational training
-
Public healthcare services
-
Life insurance policies
-
Transfer of land use rights
Note: Even when VAT is exempt, businesses may still be required to file VAT declarations periodically.
How to Register for Value-Added Tax (VAT)
Registering for Value-Added Tax (VAT) in Vietnam is a legal requirement for both local and foreign-invested businesses engaged in taxable activities. Below is a detailed, step-by-step guide to help your company navigate the VAT registration process in Vietnam in 2025.
Step 1: Business Registration and Tax Identification
Before you can register for VAT, your company must be legally established in Vietnam.
-
Obtain a Business Registration Certificate (BRC)
-
Issued by the Department of Planning and Investment (DPI) after company incorporation.
-
This certificate proves your business is legally recognized in Vietnam.
-
-
Receive a Tax Identification Number (TIN)
-
Automatically issued upon business registration.
-
The TIN is essential for all tax-related filings, including VAT.
-
-
Complete VAT Registration
-
VAT registration must be submitted within 10 working days from the date your enterprise receives the BRC.
-
Registration is done via the General Department of Taxation’s electronic tax system (eTax) or through a certified accounting/tax service provider.
-
Step 2: Set Up Your E-Invoice System
As of 2025, electronic invoicing (e-invoice) is mandatory for all businesses operating in Vietnam.
-
Companies must register and issue e-invoices through:
-
The national e-invoice portal operated by the General Department of Taxation (GDT), or
-
An authorized e-invoice service provider.
-
-
E-invoices must include:
-
Your VAT rate (0%, 5%, or 10%)
-
Buyer and seller information
-
Digital signature
-
Timestamps per GDT regulations
-
Compliance Tip: Ensure your e-invoice software is fully integrated and GDT-approved to avoid penalties.
Step 3: Choose VAT Filing Frequency
Businesses must choose a VAT filing frequency based on their annual revenue:
-
Monthly VAT Filing:
-
Required for businesses with annual revenue exceeding VND 50 billion (approx. USD 2 million).
-
VAT declarations and payments are due by the 20th of the following month.
-
-
Quarterly VAT Filing:
-
Allowed for businesses with annual revenue of VND 50 billion or less.
-
Declarations and payments are due by the 30th of the month following the end of each quarter.
-
The tax authority determines your filing cycle based on your previous fiscal year’s revenue or your first year’s projected revenue.
Calculating Value-Added Tax (VAT)
Understanding how to calculate your VAT payable in Vietnam is essential for accurate tax reporting and compliance. The Vietnamese VAT system is credit-based, meaning businesses offset the VAT they collect (output VAT) with the VAT they pay on their purchases (input VAT).
VAT Calculation Formula in Vietnam
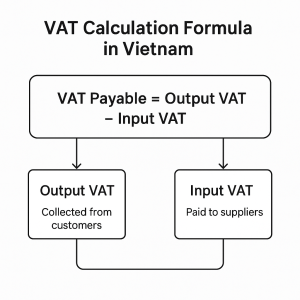
VAT Payable = Output VAT – Input VAT
-
Output VAT: The amount of VAT your business collects when selling taxable goods or services.
→ Formula: Selling Price × Applicable VAT Rate (10%, 5%, or 0%) -
Input VAT: The VAT your business pays when purchasing goods or services from suppliers for business use.
→ Can be credited if proper invoices and documentation are available.
VAT Calculation Example
Let’s say your company in Vietnam had the following transactions in a given month:
-
Total Sales Revenue: VND 200 million
→ Applicable VAT Rate: 10%
→ Output VAT = 200 million × 10% = VND 20 million -
Purchases from Suppliers: VND 80 million
→ Includes goods and services used for business operations
→ Input VAT = 80 million × 10% = VND 8 million
VAT Payable = Output VAT – Input VAT = 20 million – 8 million = VND 12 million
Your business will need to declare and pay VND 12 million to the tax authority for that period.
Common VAT Filing Errors and Solutions
Proper VAT declaration is critical to avoid tax penalties and audits. Here are the most common VAT filing mistakes in Vietnam, along with practical solutions:
1. Incorrect or Invalid E-Invoices
-
Issue: Using the wrong invoice format or unregistered e-invoice platforms.
-
Solution: Always use e-invoicing software approved by the General Department of Taxation (GDT) or licensed providers authorized by the Ministry of Finance.
2. Neglecting to Record Input VAT
-
Issue: Missing or disorganized invoices means lost VAT credits.
-
Solution: Keep all input VAT invoices and receipts properly recorded and filed. Ensure they are valid (with digital signatures and correct buyer/seller info).
3. Applying the Wrong VAT Rate
-
Issue: Misclassifying goods/services and applying 10% instead of 5% or 0%.
-
Solution: Consult a tax advisor or cross-check with GDT guidance to confirm the correct VAT rate for each item or service.
4. Missing VAT Declaration Deadlines
-
Issue: Late filings can result in penalties and interest charges.
-
Solution: Use automated accounting software, tax compliance platforms, or set up calendar reminders to stay on schedule.
Pro Tip for Businesses:
-
Always reconcile your VAT ledger monthly.
-
Conduct periodic internal audits to ensure compliance.
-
Stay updated with the latest VAT regulations in Vietnam (Circulars, Decrees, and tax authority announcements).
Claiming VAT Refunds in Vietnam
In Vietnam, businesses may be eligible to claim a VAT refund when their input VAT exceeds output VAT, particularly in cases involving export activities or large capital investment projects. The Vietnamese government allows for VAT refunds to help ease cash flow pressure and support business growth.
Who Can Claim a VAT Refund?
You may qualify for a VAT refund in Vietnam if your business meets one of the following conditions:
-
Input VAT Exceeds Output VAT (for Exporters):
-
Export-oriented businesses often pay high input VAT on purchases (e.g. raw materials) while charging 0% VAT on exports.
-
This creates a refundable VAT credit balance.
-
-
New Investment or Expansion Projects:
-
Companies that are in the setup phase or undertaking large-scale expansion may accumulate significant input VAT before generating revenue.
-
Refunds can be requested to ease the financial burden.
-
-
Projects with Long Investment Cycles:
-
Enterprises investing in infrastructure, factories, or machinery before operations begin can claim refunds based on input VAT incurred.
-
Minimum refund value: VND 300 million
Processing time: Approximately 20 to 40 working days after submission of a complete and valid refund dossier.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with VAT regulations in Vietnam can lead to monetary penalties, delayed refunds, or even tax audits. Below is a summary of common violations and their associated penalties:
| Violation | Penalty |
|---|---|
| Late VAT filing or declaration | VND 2 – 25 million |
| Filing incorrect VAT returns | Up to 20% of the understated or underpaid VAT amount |
| Failure to issue valid e-invoices | Heavy administrative fines and potential audit/investigation |
| Using unlicensed e-invoicing platforms | May result in rejection of input VAT and legal penalties |
Best Practices for ManagingValue-Added Tax (VAT)
To ensure proper VAT compliance and minimize tax risks, businesses should adopt the following VAT management strategies:
-
Maintain Accurate and Real-Time Accounting Records
-
Use digital accounting systems integrated with Vietnam’s tax portal to record VAT transactions and issue valid e-invoices.
-
-
Set Reminders for Filing Deadlines
-
Avoid late submissions by creating an internal calendar for monthly or quarterly VAT returns.
-
-
Conduct Monthly VAT Reconciliations
-
Match input VAT invoices with purchases, and output VAT with sales to identify discrepancies before submission.
-
-
Coordinate with Foreign Contractor Tax (FCT) Obligations
-
If engaging foreign service providers, determine whether your company must withhold and declare VAT on their behalf.
-
-
Seek Expert Tax Advisory for Complex Issues
-
Consult with licensed tax advisors or accounting firms for guidance on VAT refunds, exemptions, cross-border services, or audits.
-
Final Thoughts
Understanding and complying with Vietnam’s VAT system is crucial for financial health and legal compliance. By registering on time, calculating VAT accurately, meeting filing deadlines, and keeping complete records, businesses can avoid penalties and benefit from refunds.
Need help with VAT in Vietnam? Contact Green NRJ for expert assistance with VAT registration, reporting, refunds, and long-term compliance strategy.






